Introduction
Ankle pain is a condition that occurs in the ankle and its joints, affecting movement and daily activities. In some cases, the pain may be so severe that bearing weight on the ankle becomes impossible, leading to difficulty walking or an inability to walk.
Symptoms
- Acute Pain Pain that occurs immediately following an injury or accident, such as an ankle sprain.
- Chronic Pain Pain that lasts for an extended period or recurs intermittently.
- Swelling The ankle may swell and feel painful.
- Skin Color Changes The ankle may appear red, blue, or black.
- Discomfort or Tingling Sensation A tingling, numbness or uncomfortable feeling in the ankle.
Causes
- Ankle Sprain Torn or overstretched ligaments around the ankle due to twisting or excessive stretching.
- Fractures A break in the bones around the ankle, often resulting from a fall or severe injury.
- Tendinitis Inflammation of the tendons, such as Achilles tendinitis, usually caused by overuse.
- Arthritis Pain and inflammation in the ankle joint, such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout.
- Infections in the ankle can cause swelling and pain.
- Stress Fractures Fractures caused by repetitive stress without adequate rest.
- Flat Feet or High Arches Structural changes in the feet that can cause stress on the ankle.
- Muscle Imbalance An imbalance in muscle strength can lead to stress in the ankle.
Physical Therapy Treatments
Pain and Inflammation Relief:
- Cold Therapy: Applying ice packs to reduce swelling and inflammation during the initial phase.
- Heat Therapy: Applying heat to relieve tension after the inflammation phase.
- Electrical Stimulation (TENS): Low electrical currents are used to relieve pain.
- Ultrasound: Enhances blood circulation and alleviates pain.
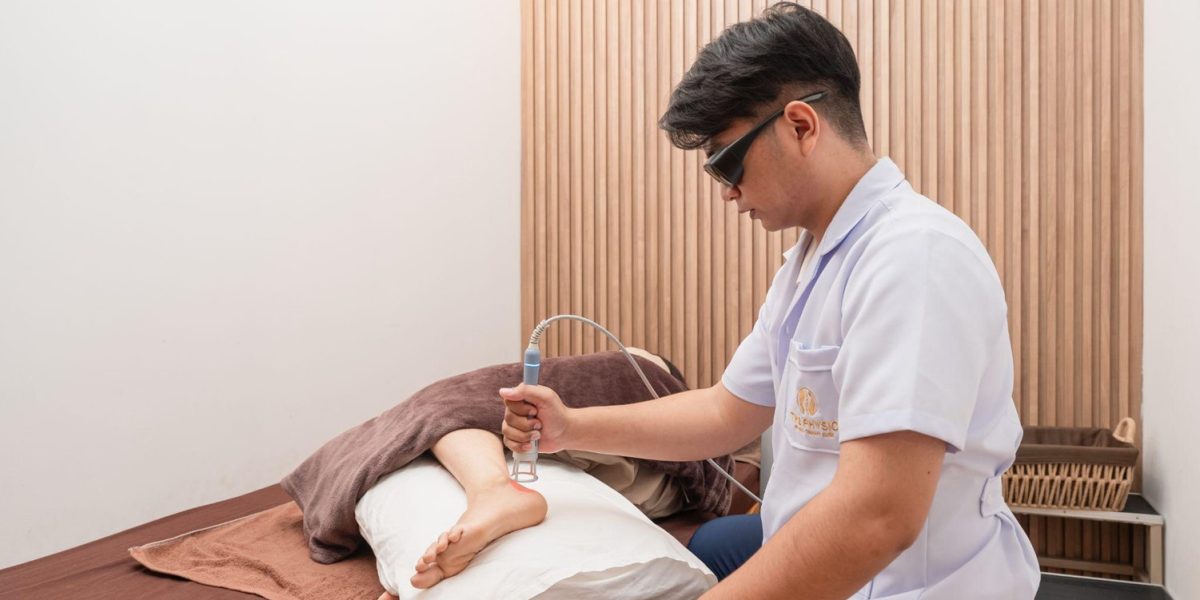
- High Power Laser Therapy: Stimulates tissue repair.
- Shockwave Therapy: Promotes tissue repair and new blood vessel formation.
Exercise and Rehabilitation:
- Strengthening Exercises: Such as leg lifts and muscle stretching.
- Range of Motion Exercises: Rotating and stretching the ankle.
- Balance and Proprioception Training: Enhancing balance and awareness of ankle position.
Use of Assistive Devices:
- Braces and Supports: Ankle braces to reduce pressure on the joint.
- Orthotics: Shoe inserts or devices to support the feet.
Gait and Posture Training:
- Gait Training: Practicing correct walking techniques to prevent injury.
- Posture Correction: Practice proper posture to reduce stress on the ankle.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can flat feet be corrected?
Treatment for flat feet usually focuses on alleviating symptoms and improving foot function rather than a complete cure. However, appropriate care can effectively reduce symptoms and enhance quality of life.
How long does it take to recover from plantar fasciitis?
- Mild to Moderate Cases: Typically, recovery takes about 6-8 weeks with proper treatment and adherence to recommendations.
- Severe Cases: May take longer, often 3-6 months or more, depending on the severity of the condition and the response to treatment.

