Introduction
Low back pain refers to discomfort in the lower back, including tightness in the back muscles or stiffness in the area from the lower rib cage to the buttocks. In some cases, the pain may radiate down the legs. This condition can arise from degenerative diseases and issues affecting the muscles, ligaments, bones and intervertebral discs, including the following:
- Degenerative Disc Disease: As individuals age, intervertebral discs can deteriorate, develop cracks, or lose fluid, leading to back pain. Some individuals may remain asymptomatic despite disc degeneration.
- Herniated Disc: Damage to a disc can cause it to protrude and compress nearby nerves, resulting in pain that radiates from the hip down the leg. This condition may resolve on its own as the tissues heal.
- Degenerative Osteoarthritis: Lower back pain can occur due to bone spurs caused by facet joint degeneration related to aging.
- Spondylolisthesis: Pressure on the lower back joints can cause the spine to shift forward, resulting in back pain and pain radiating to the hips and legs.
- Spinal Stenosis: Bone spurs may narrow the spinal canal. Some individuals may experience leg pain while walking, while others may show no symptoms.
- Ankylosing Spondylitis: This condition, which causes lower back pain in adolescents and young adults, can lead to stiffness and reduced movement if left untreated.
Symptoms
Low back pain can be categorized by duration:
- Acute Low Back Pain: Pain that persists for less than six weeks.
- Subacute Low Back Pain: Pain that lasts more than six weeks but less than three months.
- Chronic Low Back Pain: Pain that continues for more than three months.
Causes
Several factors can contribute to low back pain, including:
- Weak Muscles: Weakness in the core muscles and reduced stability.
- Poor Posture: Repetitive and prolonged activities, such as in office workers or athletes.
- Accidents or Injuries: Falls, improper lifting techniques, or sports-related injuries.
- Spinal Abnormalities: Including degenerative disc disease and scoliosis.
- Other Factors: Pregnancy, obesity, kidney issues, ovarian and uterine disorders, prostate problems, cancer spread and psychological factors such as stress and depression.
Physical Therapy Treatments
Several methods can help alleviate low back pain:
1. Heat and Cold Therapy:
Cold packs can be used initially after an injury to reduce swelling and pain, while heat can help relax tense muscles.
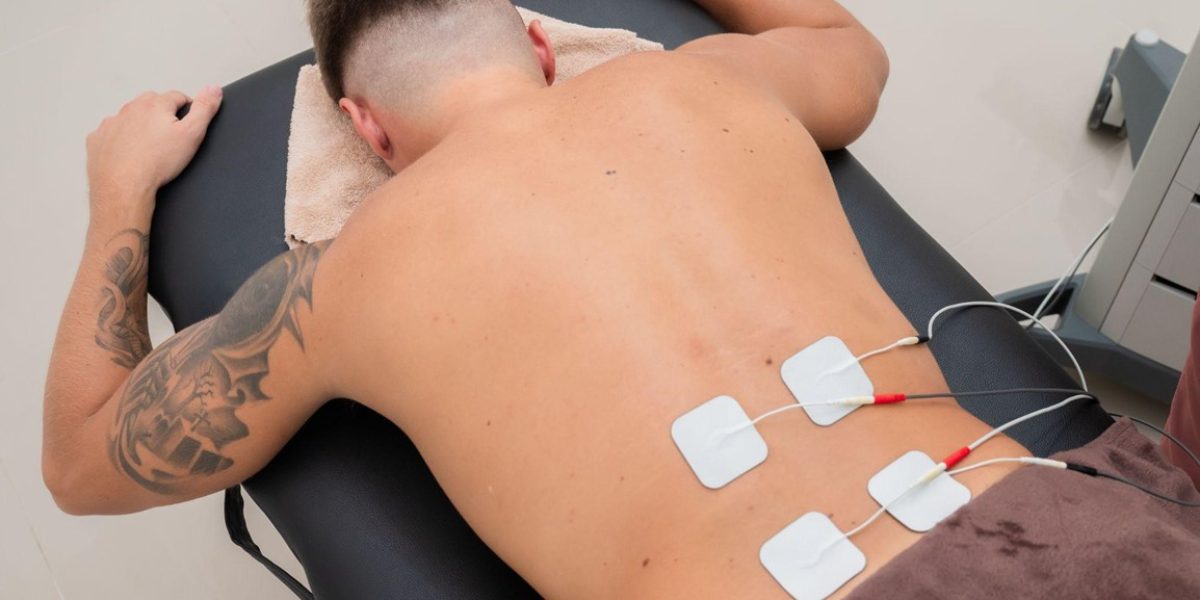
2. Electrical Stimulation (TENS):
Helps reduce pain and stimulate blood circulation.
3. Ultrasound Therapy (US):
Increases blood flow and aids in tissue repair.
4. Peripheral Magnetic Stimulation (PMS):
Reduces pain, relaxes muscles and strengthens muscle function.
5. Shockwave Therapy (SWT):
Stimulates tissue repair and reduces muscle pain.
6. High Power Laser Therapy (HPLT):
Enhances blood circulation and aids tissue repair.
7. Stretching and Exercise:
Reduces muscle tightness and increases flexibility.
8. Manual Techniques:
Helps reduce tension and alleviate pain.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I prevent low back pain?
Regular exercise and movement are effective ways to prevent recurrence of low back pain. Strengthening the core and hip muscles and learning proper lifting techniques (such as engaging the core and bending the knees when lifting heavy objects) are beneficial. Additionally, frequently changing positions while standing or sitting for extended periods can prevent muscle tension.
What should I do if I experience back pain while sleeping?
Check if your mattress and pillow are suitable. The mattress should neither be too soft nor too firm and the pillow should support your head and neck in alignment. If you sleep on your back, use a pillow under your knees and if you sleep on your side, slightly bend your knees and place a pillow between your legs to effectively reduce back pain.
How should I lift heavy objects if I experience back pain?
Back pain from lifting heavy objects is common, as many individuals often lift heavy items improperly in daily life. The best solution is to lift objects correctly by first assessing if you can handle the weight. Then, bend your knees while keeping your back straight, lift the object without extending your arms, keep your head aligned and use your thigh muscles to push yourself up. When placing the object down, repeat the steps by bending down, keeping your back straight and carefully placing the object down.

